External events
Seismic event analysis:
- Two types of seismic event analyses:
- – Seismic Margin Analysis (SMA),
- – Seismic PSA (SPSA).
- SMA is a deterministic analysis to show that the plant is able to withstand a seismic event with given acceleration.
- The SPSA method is currently the most practical method of addressing questions such as:
- 1 . What is the seismic risk to the plant?
- 2 . What range of ground motion levels dominate the seismic risk?
- 3. What plant components are dominant contributors to seismic risk?
Main steps of SPSA:
- Probabilistic seismic hazard analysis - used to identify the seismic risk of the site.
- Fragility analysis - used to identify the seismic capacity of structures, systems and components.
- Seismic PSA development - used to quantify the seismic risk.
Natural events other than seismic events:
- After a screening process the following natural external events are considered for the Slovak NPPs in the EEPSA: extreme wind loading, tornado, extremely low and extremely high outside temperatures, extreme rainfall, snow conditions and site flooding, icing and lightning,
- Credible combinations of individual events, including internal and external hazards, that could lead to anticipated operational occurrences or design basis accident conditions, must be also considered. Engineering judgment and probabilistic methods can be used for the selection of the event combinations.
- Non-seismic external event PSA, main steps:
- - Construction of hazard curves.
- - Fragility analysis.
- - Development of the PSA model.
For illustration fragility curves for extreme wind are presented for a building of the plant in Fig.1. Hazard curves for extremely low temperatures for the plant site are presented on Fig. 2.
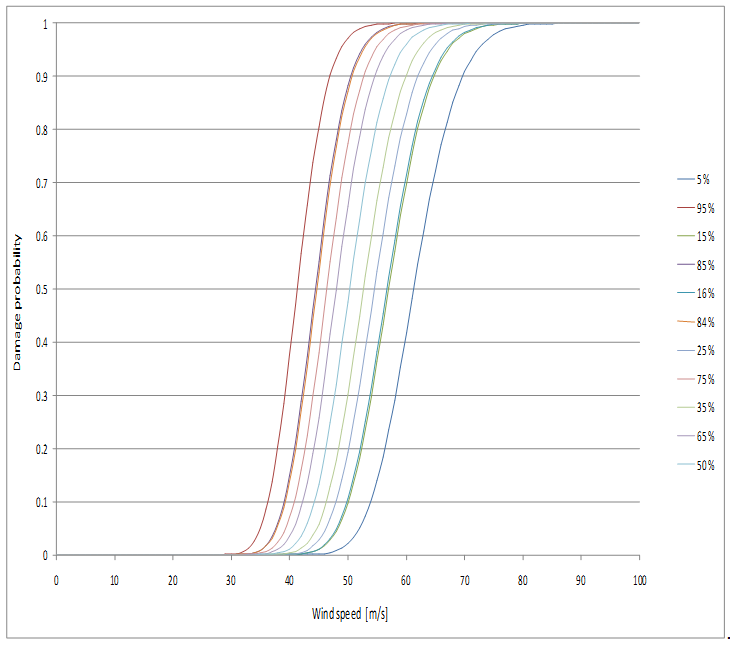
Fig 1. Fragility curve for extreme wind of a building
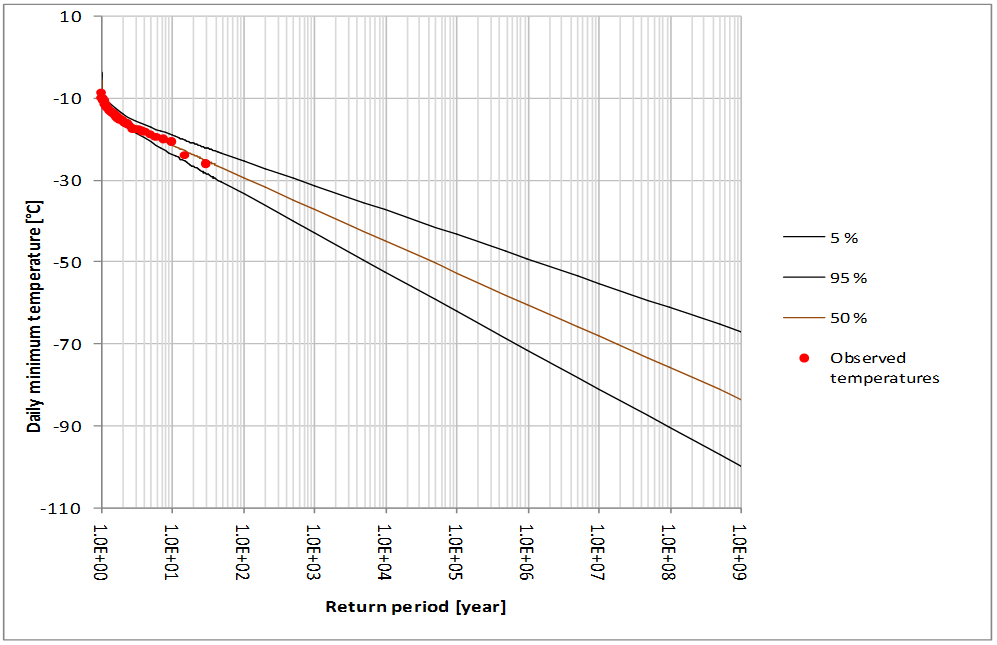
Fig 2. Hazard curves for extreme wind on the site
RELKO Ltd., Račianska 75, P.O.Box 95, 830 08 Bratislava
